▎雙投影結合全景深度偵測
BiFuse: Monocular 360 Depth Estimation via Bi-Projection Fusion
►國立清華大學 孫民副教授 / Associate Prof. Min Sun, National Tsing Hua University
(CVPR 2021 Oral 接受率: 4%)
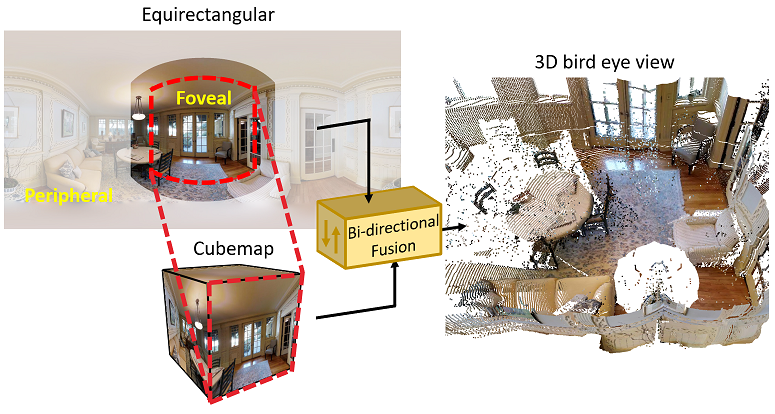
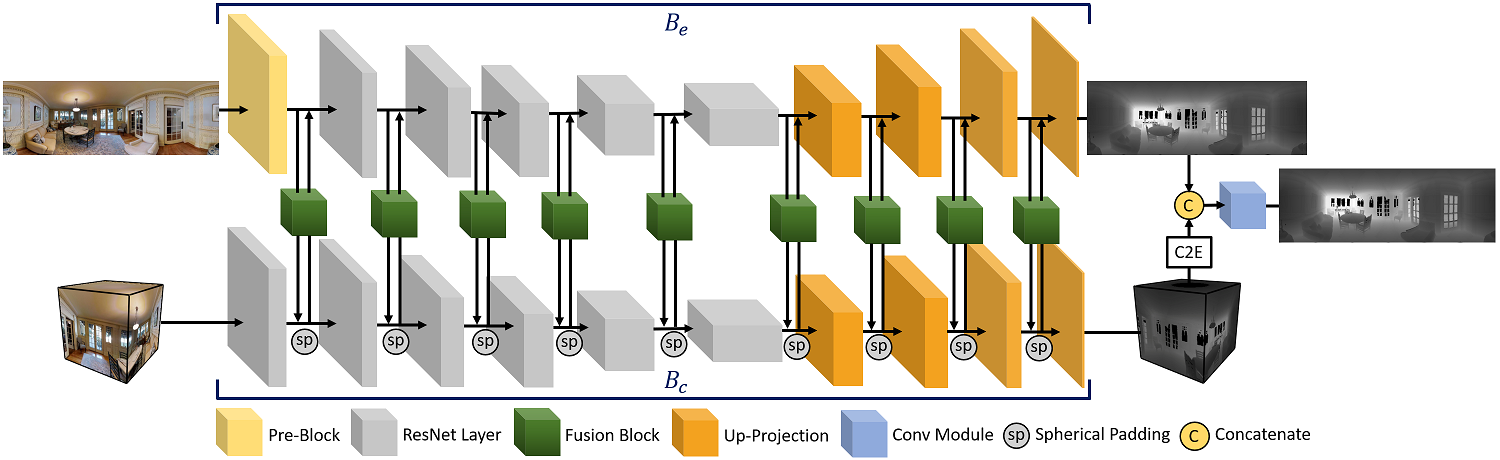
因為全景影像具有嚴重扭曲的關係,將現有深度學習技術直接運用在全景影像上會導致訓練結果不如預期,透過將全景影像轉換成不同投影方式並相做結合能使得訓練更穩度並達到更精準的深度預測結果。
特色:
- 透過立方轉換投影來解決全景圖南北極扭曲的問題。
- 透過等距長方投影使網路能得到全局的資訊。
- 透過結合不同的投影方式能夠更精準的預測全景影像的深度。
- 所提出的雙投影結合模組能夠有效率的整合不同投影的特徵圖進而提升準確度。
(CVPR 2021 Oral Acceptance Rate: 4%)
Due to the distortion introduced by equirectangular projection, simply applying deep neural networks on the panoramas usually results in a sub-optimal training result. Hence, we propose to combine the feature maps from different projection types to help the network to learn feature maps of different types.
In general, our contributions are listed as following:
- We use cubemap projection to solve the distortion introduced by equirectangular projection.
- We use equirectangular projection to provide the global contextual information to the networks.
- Using different projections can significantly improve the performance.
- We propose the “bi-projection fusion” module that is capable of efficiently integrating feature maps from different projection types and thus improve the accuracy of depth estimation.
Reference :
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 1 2項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 12 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎物件個體共同切割
Instance Co-segmentation
► 國立清華大學 林嘉文教授 / Prof. Chia-Wen Lin, National Tsing Hua University
影像切割是核心電腦視覺應用,但需要倚賴大量以像素為標註單位的訓練影像。針對此議題,我們提出一個嶄新的研究議題:物件個體共同切割(instance co-segmentation),即在多張圖中,以個體(instance)為單位切割出共同類別之物件,該議題設定創新性在於:1)這是一個嶄新且實用的研究議題;2)用共同分割的形式進行,故避免深度學習資料標註的問題;3)它兼顧物件個體 與類別,可提供後續應用更多的資訊。我們在論文提出一個有效的深度學習演算法實現物件個體共同切割,論文在CVPR’19以口語報告形式發表(oral presentation),並入圍大會最佳論文獎(best paper finalist)。
Object segmentation is essential in computer vision, but it relies on a large amount of training images with pixel-level annotations. To address this issue, we present instance co-segmentation, where we aim at identifying and segmenting all object instances of a category commonly present in multiple instances.
The main contribution of this work is three fold: 1) It is a novel and practical research topic; 2) It carries out co-segmentation, hence alleviating the issue of the high annotation cost in object segmentation; 3) It provides follow-up applications with both instance- and class-specific information. We present a deep learning algorithm to realize instance co-segmentation in the paper, which is selected as oral presentation in CVPR’19 and is in the Best Paper Finalist.
Reference :
▲兩個物件個體共同切割的例子,其中共同的物件類別分別為鳥和羊,物件個體分別為一隻鳥和一頭羊。在每一例中,上排四張為輸入影像,下排四張是使用我們方法所得到的切割結果,其中不同顏色代表我們方法所能識別出的不同物件個體。
Two examples of instance co-segmentation on categories bird and sheep, respectively. An instance here refers to an object appearing in an image. In each example, the top row gives the input images while the bottom row shows the instances segmented by our method. The instance-specific coloring indicates that our method produces a segmentation mask for each instance.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 20 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 20 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎人工智慧胰臟癌輔助偵測系統
PANCREASaver
► 國立臺灣大學王偉仲教授 / Prof. Weichung Wang, National Taiwan University
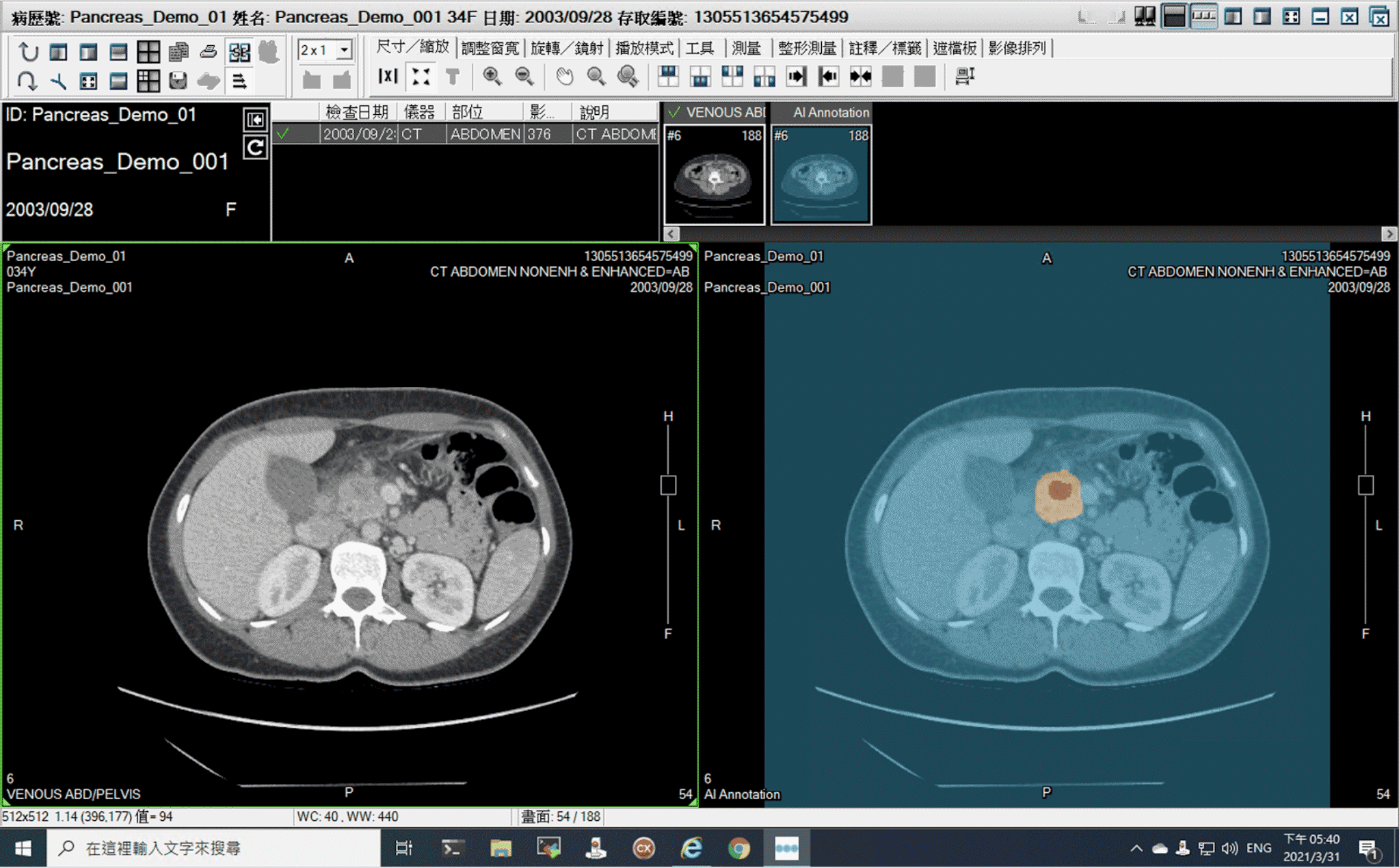
電腦斷層影像是偵測胰管腺癌(發生率最高的一種胰臟癌)最主要的方式。然而小於 2 公分的胰管腺癌在電腦斷層影像上難以辨識,約 40% 被遺漏,且多數早期胰臟癌的症狀不明顯,容易因遺漏而錯失治療契機。本團隊開發人工智慧胰臟癌輔助偵測系統 是一款全自動的電腦輔助偵測系統,以電腦斷層影像檔作為資料集,利用深度學習模型偵測是否有胰臟癌。本系統在偵測胰臟癌的表現上,敏感度高於放射科醫師,能正確地找出 92% 放射科醫師未發現的胰臟癌,對小於 2 公分的胰臟癌也有高達 92.1% 的敏感度,以上成果已發表在國際期刊《刺胳針數位醫療》。
Computed tomography (CT) is the major imaging modality for detection/diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, accounting for 90% of pancreatic cancer (PCs)), but small PDACs are often obscure, with approximately 40% of tumors <2 cm being missed on CT. We have developed a novel artificial intelligence (AI)-empowered computer-aided detection (CAD) tool, PANCREASaver, to assist radiologists in detecting PCs.
PANCREASaver is a fully automatic end-to-end CAD tool which employs deep learning models to predict whether CT images harbor PC and indicate the predicted location of the PC, without the need for preprocessing of the images by radiologists. It is able to detect 92% of the PDACs missed by radiologists, with 92.1% sensitivity for tumors less than 2 cm (published in The Lancet Digital Health, 2020).
Reference :
◀ 人工智慧胰臟癌輔助偵測系統能夠同時顯示原始影像及模型預測之胰臟與腫瘤區域(橘色部分為系統標註之胰臟,紅色部分為系統標註之腫瘤位置)。
PANCREASaver can display the pancreas and tumor regions of the original image and the prediction model simultaneously (the orange part represents the pancreas marked by the system, and the red part is the position of the tumor marked by the system).
◀ 研究成果於 2020 年 7 月發表於《刺胳針數位醫療》,並獲選 2020 美國腸胃科年會傑出論文。
The research result was published in “The Lancet Digital Health” in July 2020, and received the outstanding paper award of Digestive Disease Week (DDW) in 2020.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 25 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 25 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎個人化精準腫瘤治療顧問
Precision Cancer Advisor
►國立臺灣大學王偉仲教授 / Prof. Weichung Wang, National Taiwan University
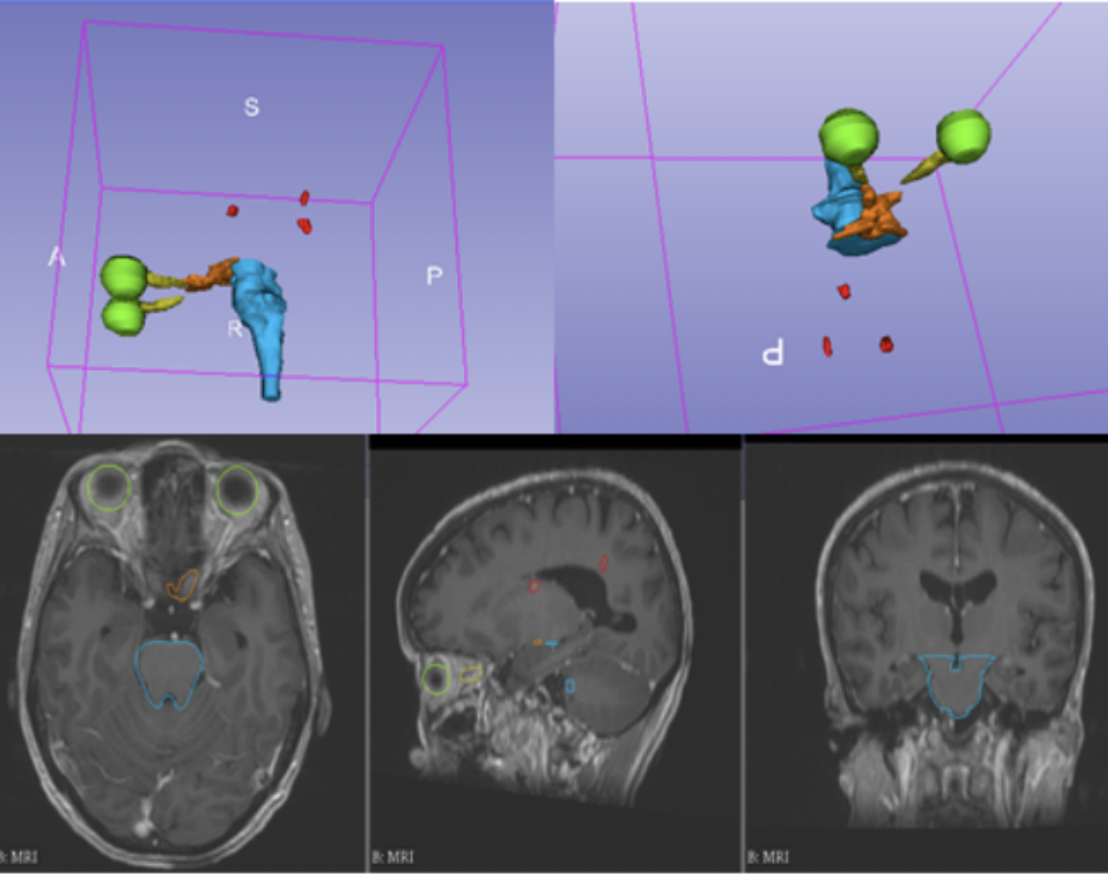
約有20%至40%的癌症患者會引發轉移性腦瘤,如何利用影像篩選適當患者,接受立體定位放射手術,避免傳統開顱手術風險或全腦放射治療帶來的認知功能缺損,是精準癌症醫學的重要課題。本團隊開發了個人化精準腫瘤治療顧問,使腦轉移腫瘤能被及早的偵測、精準的圈選以及相關預後預測。其中極具創新性的腦轉移瘤及周圍危及器官之自動標註系統,不僅提供腫瘤標註結果可信度評估給臨床醫師覆核及修正,更可協助醫師進行臨床決策與醫病溝通。
Research has shown that about 20 to 40% of cancers metastasize to the brain. While traditional craniotomy or whole brain radiation therapy can result in unnecessary risks or possible cognitive impairment, using medical image analysis to screen patients with brain metastases for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is an integral part in applying precision medicine to cancer treatment.
We have developed a high precision comprehensive SRS smart solution for brain metastases early prediction, accurate segmentation, prediction, and prognosis. Combining model architectures from Nvidia and state-of-the-art algorithms, we created an automatic labeling system for brain metastases and the surrounding organs, including eyeballs, optic nerves, etc, which is further presented to clinicians for revision and verification to improve credibility.
Reference :
◀ 個人化精準腫瘤治療顧問能夠同時標示出重要器官(綠、藍、橘色部分),以及腫瘤位置(紅色部分)
Precision Cancer Advisor is able to mark out the vital organs (green, blue, orange part) and tumor location (red part) at the same time.
◀ 本團隊與國際上多個醫學中心及 AI 廠商合作,共同進行研究,由學界帶領業界去驗證 PCA 模型。研究成果於 2020 年 8 月發表於重要國際期刊《Neuro-oncology Advances》,並獲選為 2019 年 ESMO 及 2020 年 RSNA 壁報展示,並獲得 2019 年 ESMO 年會優異獎。
We cooperate with many international medical centers and AI manufacturers to conduct joint research, which enables us to verify the PCA model in the clinical field. The research result was published in Neuro-oncology Advances in August 2020, it has also been presented at the 2019 ESMO and 2020 RSNA. Furthermore, this research was honoured with the Merit Award to the ESMO 2019 Congress.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 25 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 25 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
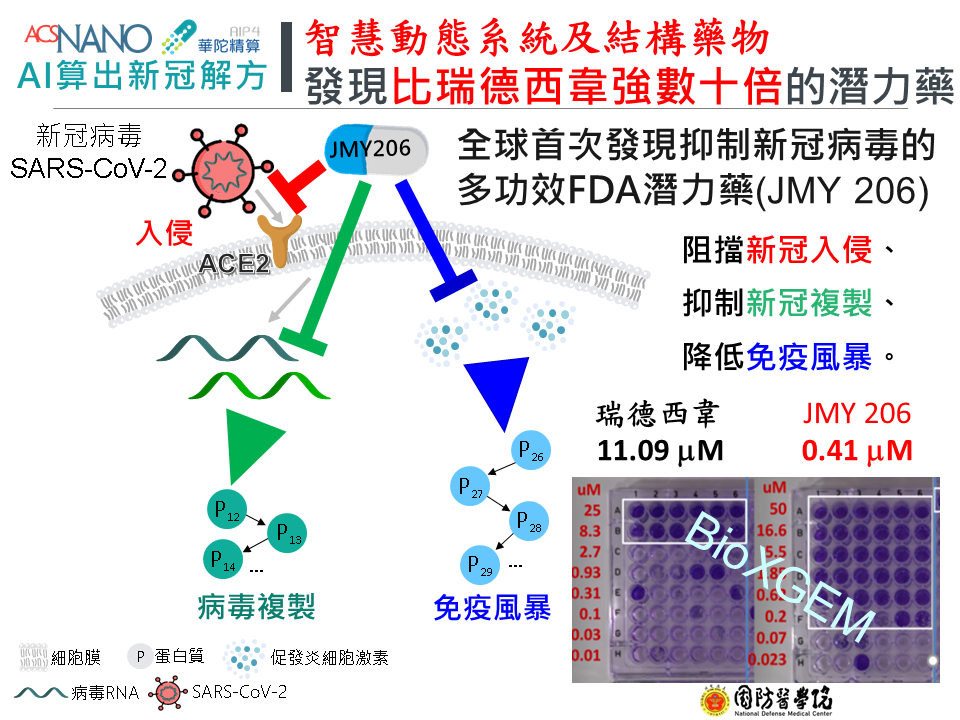
▎AI算出新冠解方
AI Identifies Promising Old Drugs For COVID-19
►國立陽明交通大學 楊進木教授 / Prof. Jinn-Moon Yang, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
新冠病毒肆虐全球,臺灣不僅防疫有成,在智慧醫療戰疫也傳出捷報!由國立陽明交大生物科技學院院長楊進木教授帶領的團隊,透過人工智慧及大數據,模擬宿主受病毒感染後的體內細胞變化機制,並比對全球超過250份已公開的冠狀病毒主要蛋白酶3D構造圖像,發現新冠病毒侵入人體細胞的關鍵蛋白質具有6種可能的動態結構,鎖定了蛋白酶的罩門,在三個月內找出具有抑制COVID-19病毒活性效果的潛力老藥,三款成果已發表於國際頂尖期刊《美國化學學會月刊:奈米領域(ACS Nano)》,開發團隊成員包含陽明交大、臺大、中央研究院、興大及國防醫學院預防醫學研究所 ,從智慧計算、細胞實驗到動物實驗,可說是國內頂尖研發力量的大型整合。
The COVID-19 pandemic is a serious global health threat, and Taiwan has succeeded in preventing the epidemic. The reported good news is form the smart medical treatment fighting against the epidemic! The team led by Professor Jinn-Moon Yang, Dean of College of Biological Science and Technology, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University(NYCU), applied artificial intelligence and big data to identify four potential old drugs that successfully inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 virus infection.
Study results for three of these compounds, have been published in the top international journal “ACS Nano”. The research team members conducted intelligent computing, cell experiments, and animal experiments and are affiliated to NYCU, NTU, Academia Sinica, NCHU, and the Institute of Preventive Medicine of NDMC,which demonstrates a great integration of domestic top R&D forces.
Reference :
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 29 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 29 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix