▎強化學習中的策略遷移
Toward Robust Long Range Policy Transfer
►國立清華大學 孫民副教授 / Associate Prof. Min Sun, National Tsing Hua University
(AAAI 2021 接受率: 21%)
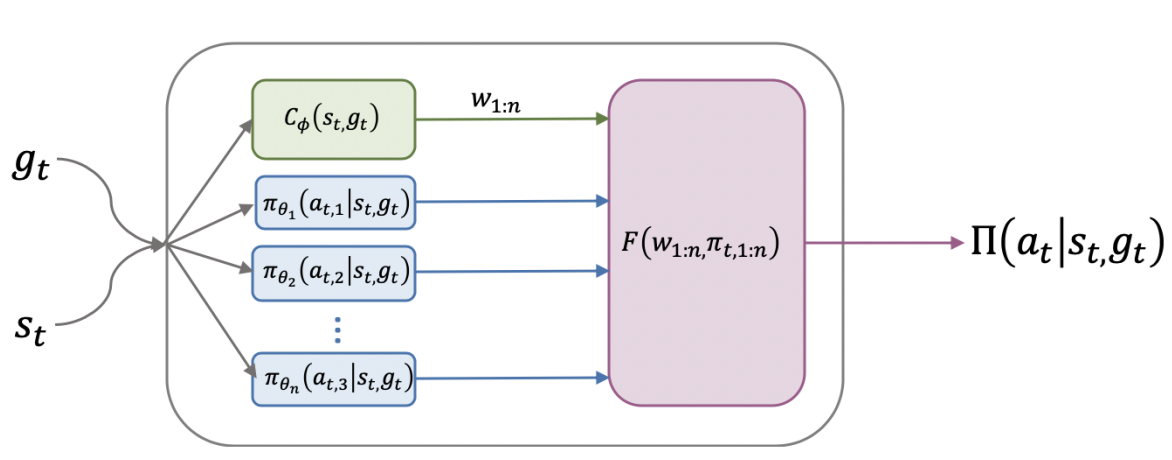
強化學習解決馬可夫決策過程(MDP)常用的方法,然後強化學習的訓練過程需要策略與環境進行多次互動,為了降低學習所需要的互動次數,我們提出適合強化學習的遷移學習
特色:
- 我們運用階級式策略學習預訓練任務,在遷移到遷移任務時,我們交替微調上層與下層的冊略
- 我們提出兩項正規目標函數來提昇下層策略的多樣性與運用效益的平衡
(AAAI 2021 acceptance rate: 21%)
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is one of the well-known approaches to solve Markov Decision Process (MDP). However, RL requires lots of interaction between policy and environment. To alleviate this issue, we propose transfer learning for RL scenario.
Our contribution is summarized below:
- We leverage hierarchical policy to solve pre-training task. For the transferring task, we alternatively high-level and low-level policy.
- We design two regularization terms to enhance the diversity and utilization rate of the low-level policy.
- Using different projections can significantly improve the performance.
Reference :
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 1 2項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 12 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎多模態情感個性運算演算法開發
Multimodal Machine Intelligence for States and Traits Computing
► 國立清華大學 李祈均副教授 / Associate Prof. Chi-Chun Lee, National Tsing Hua University
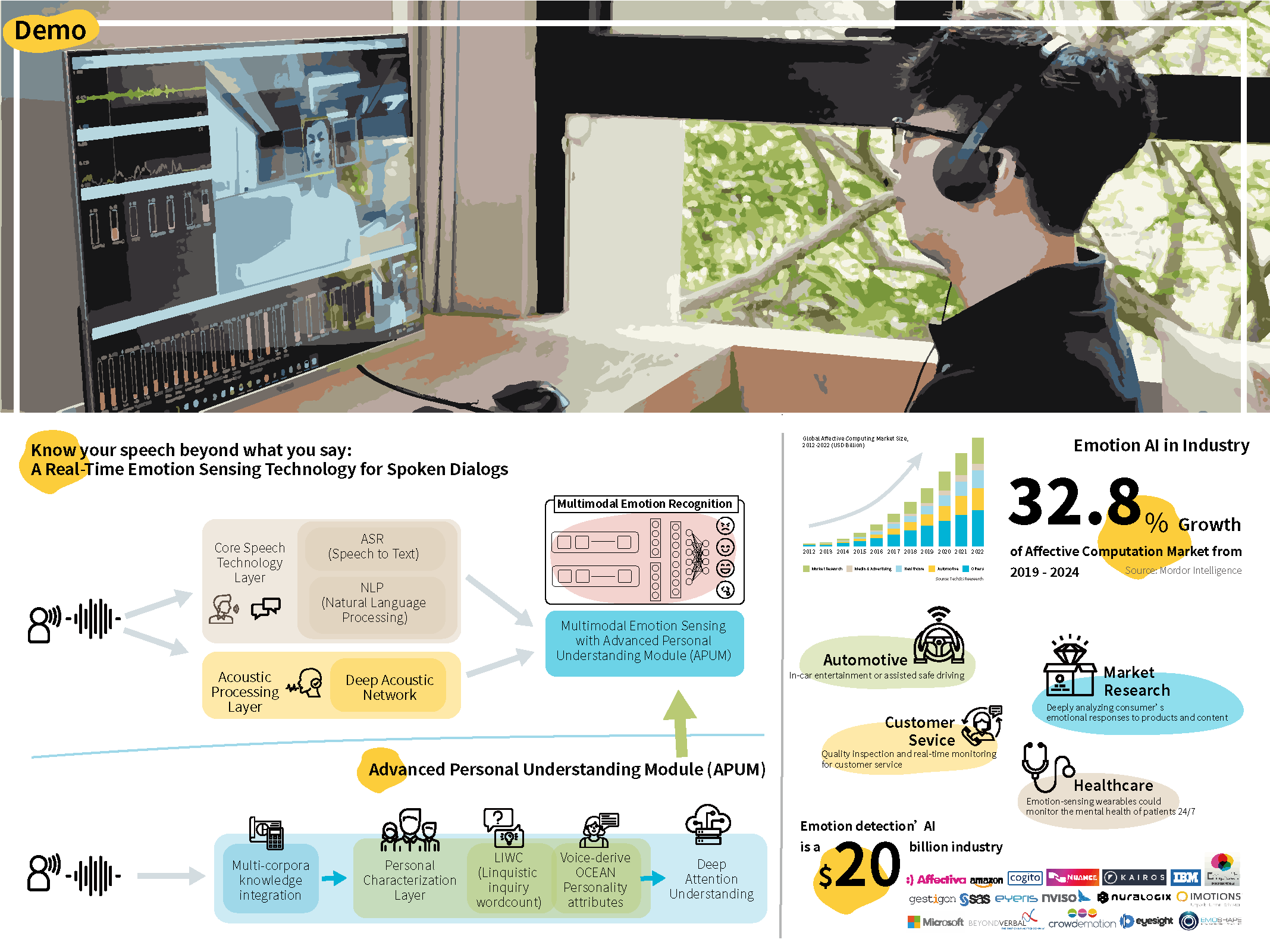
此技術整合自動語音辨識、語意分析處理、多模態融合、個人化模型的演算法,同步整合個體空間行為表徵學習,透過深度網路構建情緒辨識模組。此系統也利用語音交互之個體特性非監督式擷取技術,輔助多模態情緒辨識,讓情緒辨識架構得以適用於沒有個體特徵標記的實際應用場景。演算法架構及完整實驗結果多次發表在情感計算頂尖國際學術研討會ACII、國際最大語音技術會議INTERSPEECH、國際旗艦訊號處理會議ICASSP和相關國際學術期刊。
This technology integrates the algorithms of automatic speech recognition, context analysis processing, multimodal fusion and personalized model. It also simultaneously integrates individual spatial behavior characterization learning , and builds emotional recognition modules with deep learning network.
The system uses unsupervised retrievable acoustic embedding of personality for emotion recognition to assist multimodal emotion recognition, so that the emotion recognition structure can be applied to the real-life scenario without individual characteristic labels. The structure of the algorithms and its complete experimental results have been published in ACII, the top international academic conference on emotional computing, INTERSPEECH, the world’s largest voice technology conference, ICASSP, the international flagship signal processing conference, and related international academic journals
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 14 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 14 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎以深度神經網路辨識及分類中風步態
Detection and Classification of Stroke Gaits by Deep Neural Networks
► 國立臺灣大學 傅立成講座教授 / Chair Prof. Li-Chen Fu, National Taiwan University
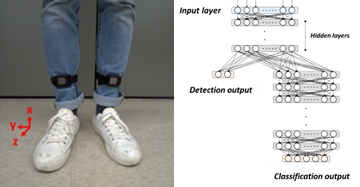
我們發展一套深度神經網路模型,以辨識及分類中風步態。中風病人癒後常發展出各種偏癱步態而需要進行復健,因為異常步態有很多種且需要針對性的醫療方針,所以如何正確地標示異常步態非常重要;臨床上異常步態的判讀分類必須仰賴於專業醫師及治療師的判斷,然而偏癱步態可能同時包含各種異常步態,而其分類常是主觀的認定,所以我們發展出一套深度神經網路模型,可以提供客觀的中風步態分類。我們首先蒐集利用慣性量測單元紀錄中風病人及一般健康人步態資料,然後我們分析這些資料來發展深度神經網路模型,以平均99.35% 的正確率辨識中風步態,並以平均97.31% 的正確率分類四種常見的異常步態:垂足、繞行、膝反屈、及抬骨盆步態。
We develop Deep Neural Network (DNN) models that can recognize stroke gaits. Stroke patients usually suffer from partial disability and develop abnormal gaits that can vary widely and need targeted treatments. Evaluation of gait patterns is crucial for clinical experts to make decisions about the medication and rehabilitation strategies for the stroke patients. However, the evaluation is often subjective, and different clinicians might have different diagnoses of stroke gait patterns.
In addition, some patients may present with mixed neurological gaits. Therefore, we apply artificial intelligence techniques to detect stroke gaits and to classify abnormal gait patterns. We applied inertial measurement units to collect clinical gait data from both stroke patients and healthy subjects. Then we analyzed these data to develop DNN models that can detect stroke gaits with an average accuracy of 99.35%. Furthermore, the developed models can classify four common gait abnormalities (i.e., drop-foor, circumduction, back-knee, and hop hiking) seen in stroke patients with an average accuracy of 97.31%.
◀ Data Measurements and the Deep Neural Networks
◀ Different patients might have different gait patterns.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 23 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 23 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎語意導向速搜特徵學習
Feature Learning for Efficient Search Via Semantics-Guided Label Prototypes
►國立臺灣大學 陳祝嵩 教授 / Prof. Chu-Song Chen, National Taiwan University
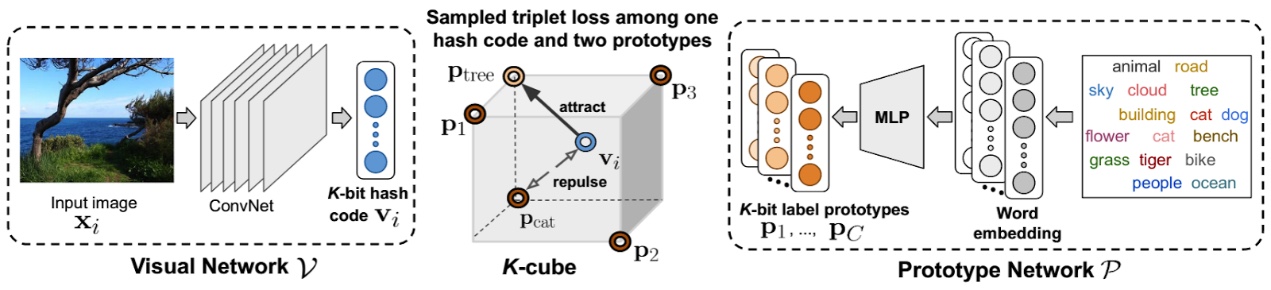
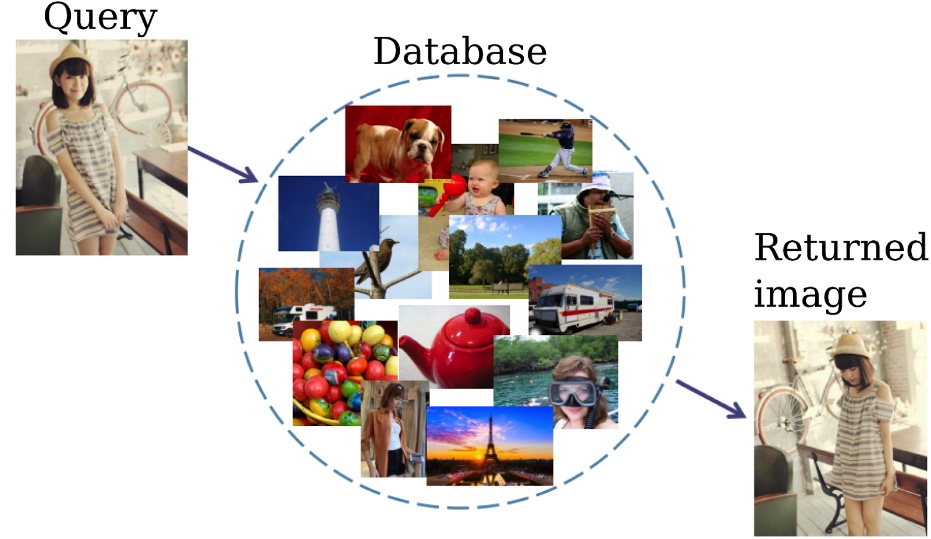
為強化巨量資料之快速搜尋與檢索。我們研發深度模型之高效特徵抽取,利用自然語言中巨量文本所訓練的語意空間(semantic space),文字和影像的概念可藉彼此模型互相校正對齊,進而讓生成的速搜特徵能在考慮影像的內容下,同時包含了人類文字概念結構,使其具相當的泛化能力以處理訓練時沒有見過的類別。本技術可協助開發影像商品搜尋模型,推廣Cambuy服務,透過影像偵測功能傳回能快速搜尋比對之雲端服務器,提供大型電商營運客戶關鍵流量導入。
Hash code learning is an important technology that enables efficient image retrieval on large-scale data. While existing hashing algorithms can effectively generate compact binary codes in a supervised learning setting trained with a moderate-size dataset, they are demanding to be scalable to large datasets and do not generalize to unseen datasets.
To overcome these limitations, we propose SemanticHash, a simple and effective deep neural network model, to leverage semantic word embeddings (e.g., BERT) in hash codes learning. Both images and class labels are compressed into few-bits binary vectors by using the visual (or the semantic) hash functions, which are jointly learned and aligned to optimize the semantic consistency. The technique is applicable to efficient search of images in huge database, enabling Cambuy services via establishing large cloud services for fast image retrieval.
Reference :
▲語意導向速搜特徵:整合語意空間與影像雜湊空間達成高效特徵學習。
Binary Feature Representation for Efficient Search Via Semantics-Guided Label Prototypes Learning
▲速搜特徵巨量影像搜尋應用:商品影像快速比對檢索
Application to efficient search of images in huge database and Cambuy.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 10 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 10 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎潛在解纏於流模型域映射
Latent Disentanglement in Flow-based Domain Mapping
►國立陽明交通大學 簡仁宗終身講座教授 / Chair Prof. Jen-Tzung Chien, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
基於流的生成模型,透過可逆轉換直接估計生成的機率分布,對似然率進行精確地推斷;亦為生成圖像提供豐富的潛在空間。而潛在變量的解纏表徵,則對於識別獨立因素和解釋圖像中的特徵有著極大幫助;使得潛在變量的不相關維度間,皆能提供獨立且有意義的特徵,可用於控制圖像合成。本研究提供以最佳化相互資訊的無監督學習方式,將潛在變量拆解為條件相關及條件無關,實現從源域到目標域的映射;並以人臉說話圖像生成為例來驗證結果。
A flow based generative model can directly estimate the generative distribution via a series of invertible transformations, precisely inferring the log likelihood, and providing a rich latent space for image generation. Latent disentanglement is crucial for identifying independent factors and interpreting image features, it enables the unrelated dimensions in the latent vector to provide independent and meaningful features, which can be used to control image synthesis.
In this research, we propose an unsupervised learning method that optimizes mutual information and decomposes the latent variables into condition-relevant and condition-irrelevant latent variables, which constructs the mapping from source domain to target domain, then we use the talking face generation as an example to evaluate our result.
Reference :
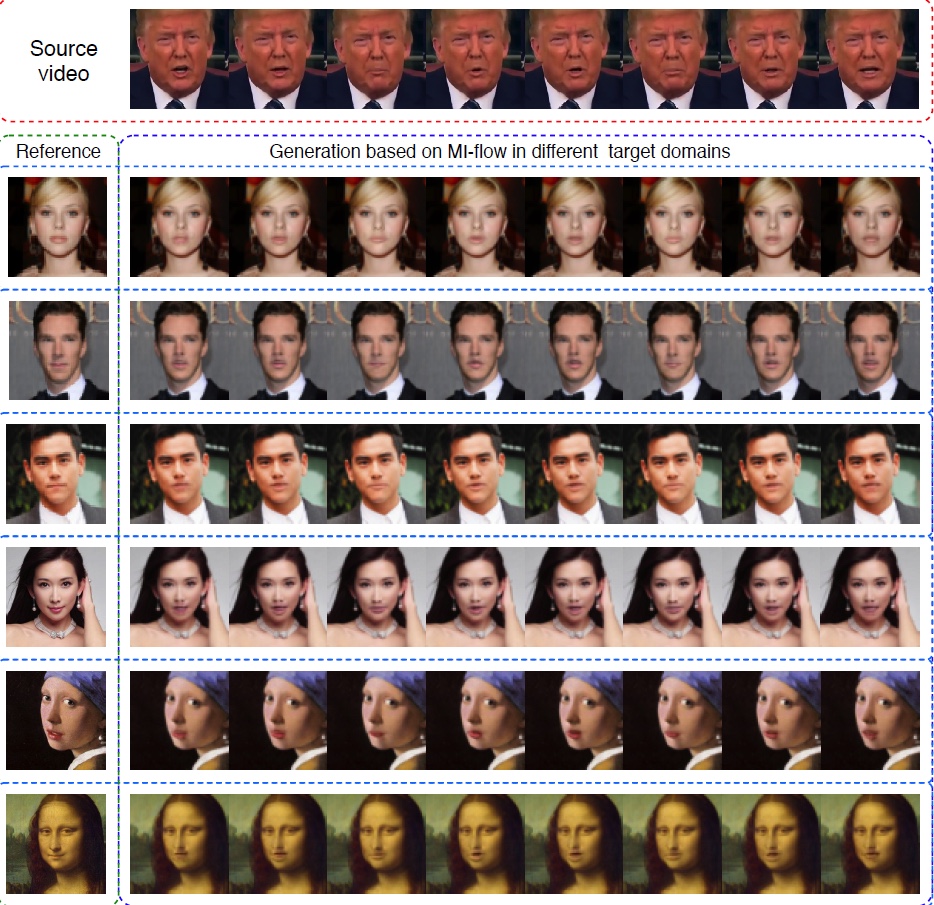
◀ 來源域為來源影片,提供條件相關的屬性,即說話嘴型;目標域為參考圖像,提供條件無關的資訊,即臉部特徵。本圖呈現從來源域映射到各個目標域的結果。
In this evaluation, the source domain is the source video. It provides the condition-relevant attribute, which is the shape of the talking mouth. The target domain is the reference image. It provides the condition-irrelevant attribute, which is the facial features. This figure shows the results of mapping from a source video to different target images.
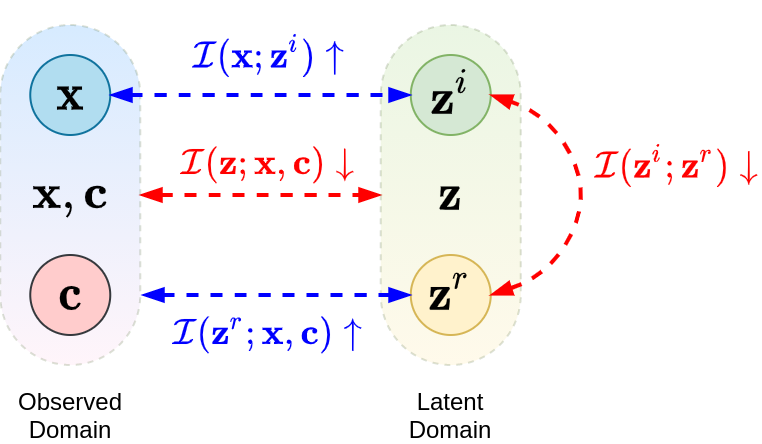
◀從來源域獲得說話嘴型-條件c,並將其映射到條件相關的潛在變量zr;參考圖片x則提供人臉特徵,將其映射到條件無關的潛在變量zi。由於希望說話嘴型與條件相關變量、人臉特徵與條件無關變量,各自配對內有所關聯,因此最大化這些配對內(c , zr)、(x , zi)的相互資訊。又因解纏需要只專注與自己有關的變量,故除了將配對內的變數相互資訊最大化以外,亦將整體的相互資訊((x,c) , z )最小化,來間接減少跨配對間的互相資訊((x , zr)或(c , zi))。另將潛在變量的(zi , zr)的相互資訊最小化,避免彼此干涉,來達到解纏的效果。
From the source domain, we obtain the shape of the talking mouth, which is the condition c, and we map it to the condition-relevant latent variable zi. We want the shape of the mouth to be related to the condition-relevant latent, and the facial features to be related to the condition-irrelevant latent, so we maximize the mutual information between these pairings ((c , zr) and (x ,zi)). On the other hand, we minimize the overall mutual information ((x,c) , z ), which indirectly reduce the mutual information between non-matching pairs ((x, zr) or (c, zi)). Finally, we minimize the mutual information between latent variables (zi, zr) to avoid interference among each other, completing the latent disentanglement.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 9 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 9 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix