▎符合OpenCL/TensorFlow API規範的終端AI理器
A GPGPU Which Supports Both OpenCL and TensorFlow Framework
►國立成功大學 陳中和教授/ Prof. Chung-Ho Chen, National Cheng Kung University
近年來人工智慧、機器學習領域快速發展,資料處理量大幅提升,通用型繪圖處理器(GPGPU)開始被廣泛運用於需要計算大量資料且可高度平行化處理的應用上。談到 GPU 大家總會想到 NVIDIA、AMD、ARM 等大型國外公司,鮮少聽到有國內廠商自行開發的 GPU,處理器是一種需要長期努力耕耘的重要基礎技術,不做或做不持續就永遠缺乏。本作品 CASLab GPU 是由成功大學電機工程學系 Computer Architecture and System Laboratory 的師生自 2013 年起規畫研製,從軟體端到硬體端完整的系統開發,目標在打造出第一顆國內自己的 SIMT 運算型 GPU。
For a long time, our local industry didn’t make continuous effort on GPU or GPGPU development and they typically out-source the GPU IP from well-known providers. However, GPU processor IP is a critical fundamental industrial technology which needs long-term effort to develop.
The aim of our work is to design and implement a GPGPU which conforms with the APIs of both OpenCL and TensorFlow framework for edge AI computing.
Reference :
圖一(fig 1.)
圖二(fig 2.)
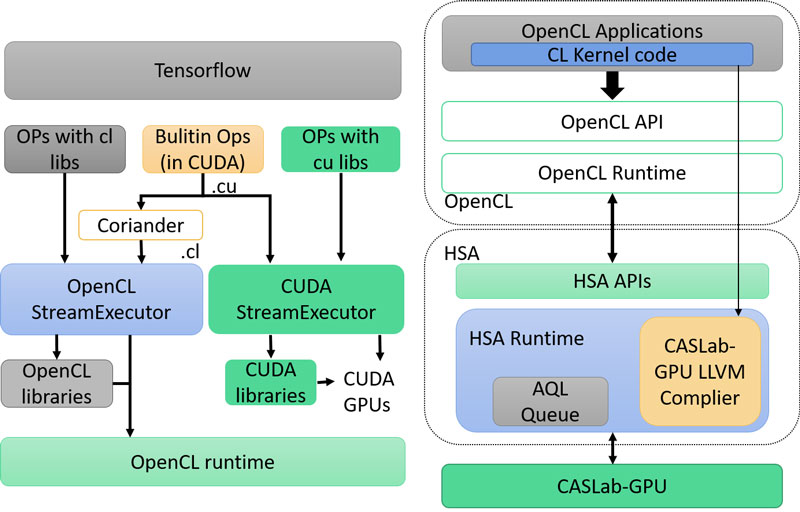
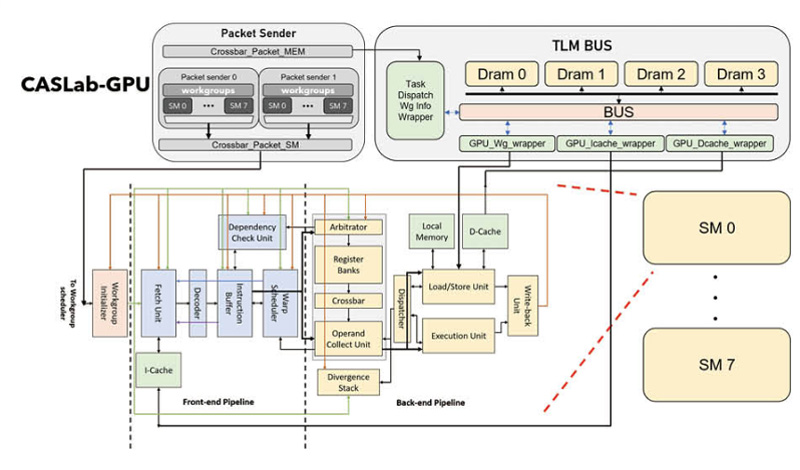
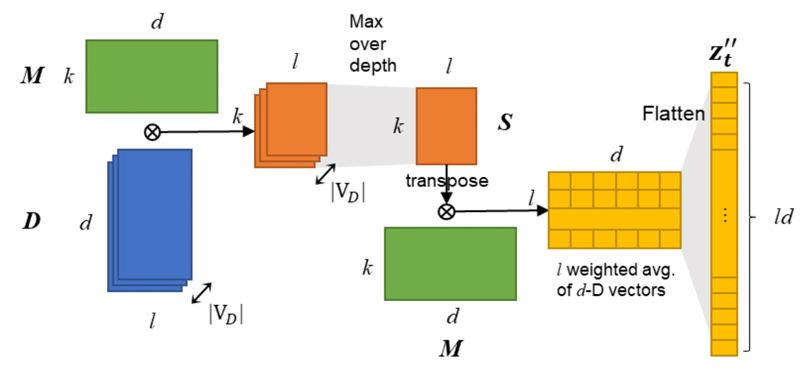
▲ CCASLab GPU (圖二)是以 Edge Computing 為目標,並符合 OpenCL/ TensorFlow API 規範,建構包含軟體及硬體的整體系統。這包括根據 OpenCL 規範設計 CASLab GPU 的 Runtime (圖一),更自行開發了CASLab GPU的OpenCL LLVM Compiler。透過優化的編譯流程,使軟體堆疊更能配合硬體的運作,獲得大幅整體效能之提升,提供開發人員便利的開源執行環境。軟體層無論是 OpenCL Runtime、 Compiler 都是由 C 程式開發,CASLab GPU 無論是搭配 ARM、 RISC-V CPU 都能夠在其平台上運作與進行應用開發。CASLab GPU 透過電子系統層級(Electronic System-Level, ESL)的 Full System 設計方案,軟體與硬體設計能在早期開發即 進行系統驗證。利用 C 與 C++ 所實作的指令級模擬器(Instruction Set Simulator,ISS)可驗證指令集的功能正確性並提供時間模型(Timing Model)來做效能上的初步評估。而使用 SystemC 高階硬體描述語言則提供彈性的硬體設計方法,因為是 Cycle Accurate 行為,開發者在早期階段就能夠更準確的分析能達到的效能,也能作為後續 Verilog RTL 的實作範本。CASLab GPU 已在 FPGA 層級完成功能性的驗證,持續的優化將讓 CASLab GPU 成為一顆更高效能的 Edge Computing IP,持續做是我們的信條。
The CASLab GPU IP (fig 2)is developed in ESL (electronic system level) design methodology. GPU software and hardware design can be verified in the early development stage. To enable TensorFlow API in the CASLab GPU, establishing a complete software stack is necessary. Fig. 1 is the software stack of the CASLab GPU. It includes the TensorFlow enabling technology, TensorFlow runtime, OpenCL runtime, LLVM OpenCL compiler, and HSA runtime. The CASLab GPU uses HSAIL-lite ISA and has its own LLVM OpenCL compiler which is currently implemented in 15,000 lines of C code in the LLVM infrastructure. The original CASLab GPU compiler is AMD CLOC with a finalizer. However, it is not specifically designed for our hardware, which leads to a performance bottleneck. The LLVM OpenCL compiler we build along with the CASLab GPU hardware has effectively increased the obtained performance of the CASLab GPU when compared with state-of-the-art commercial machine of the similar specification.
Our work, CASLab GPU, is now an FPGA functionally verified design for OpenCL data-parallelism applications e.g. Polybench, Search algorithms etc. as well as TensorFlow CNN applications. In the future, we will make continuous effort on optimizing hardware architecture, perfecting OpenCL API, supporting RNN and more AI models.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 11 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 11 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎利用二元 MRAM 的全自旋人工神經網絡
All Spin Artificial Neural Network by Binary MRAM
►國立陽明交通大學 張添烜教授/ Prof Tian-Sheuan Chang, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
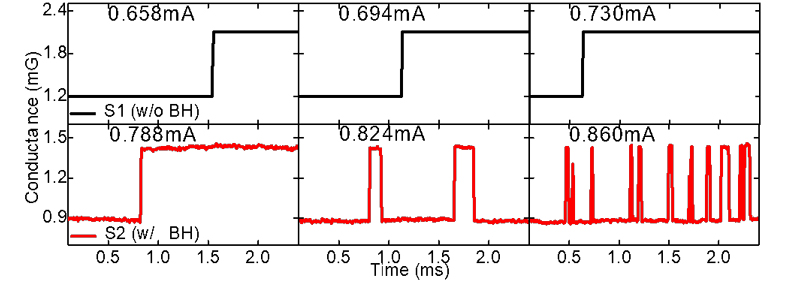
一般而言,利用 nonviolatile memory 做in-memory computing,好處是NVM 面積很小很省電,但缺點是周邊電路要做AD/DA 面積功耗都很大。我們利用MRAM 特性,電流越大,pulse 數越多,在一般memory 應用視為缺點的特性,實現in-memory computing 所需要的 ADC 的功能,做成全自旋人工神經網路硬體。我們使用MTJ中的Back Hopping振盪機制在單一元件中執行電流積分,脈衝電壓生成和重置復位等多功能,並展示出優異的四位元解析度,無電容設計且無需額外的重置電路確保最小的電路面積。
In-memory computing with nonviolatile memory achieves low
power and low area cost but also suffers from large area and power for peripheral circuits such as ADC and DAC. We propose to use the MRAM feature: higher pulse number for higher current, to realize a low cost ADC for all spin artificial neural network. We use the back hopping oscillation in MTJ to integrate current, pulse generation and reset recovery in a single device, and demonstrate excellent 4-bit precision. The final circuit shows minimum area cost with capacitor less and recovery circuit free design.
▲ 震盪元件產生的脈衝數目與電流呈正比
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 5 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 5 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎iThome 2020 臺灣資安大會設攤
Setting up a Booth on iThome 2020 Taiwan Information Security Conference
►國立臺灣大學 林宗男教授/ Prof. Tsung-Nan Lin, National Taiwan University
於本次參展中,我們展示了一套物聯網資安解決方案”Tshield”,從設備面、網路面、通訊面、資料面的角度進行保護,我們的系統包含從軟體到硬體的資安晶片(PUF硬體指紋、不可修改開機系統、端對端的加密通道、區塊鏈驗證機制、區塊儲存機制)和視覺化的管理平台具有敏捷部署、視覺化界面、即時監控、紀錄查詢、零接觸配置和第三方整合系統的特性。我們模擬台鐵火車系統作為示範場域,展示了系統沒有受到資安保護時,將容易地被駭客入侵,造成意外發生,當使用了我們的整合性系統保護時,將可以保障火車統不受駭客的破壞。
In this exhibition, we demonstrated an IoT security solution called “Tshield”,which can protect equipment, network, communication, and data. Tshield is an software and
hardware integrated chip, including PUF hardware fingerprint, non-modifiable boot system, end-to-end encryption channel, blockchain verification mechanism, block storage mechanism. In addition, there is a corresponding visual management platform which has agile deployment capability, visual interface, real-time monitoring, record query, Features of zero-touch configuration and third- party integrated systems. We simulated the Taiwan railway train system as a demonstration field, showing that when the system is not protected by information security, it will be easily invaded by hackers, causing accidents. When our integrated system protection is used, it will be able to guarantee the trains won’t be compromised by hacker’s fake identity.
▲ 模擬台鐵火車系統作為物聯網資安解決方案 ”Tshield” 示範場域圖
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 4 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 4 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎生活紀錄探勘及應用
Lifelog Mining and Applications
►國立臺灣大學 陳信希特聘教授/ Distinguished Prof. Hsin-Hsi Chen, National Taiwan University
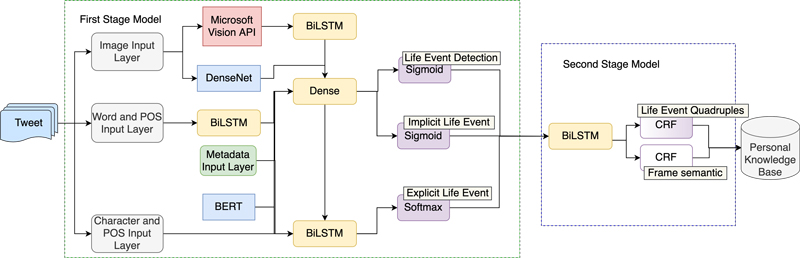
一般人日常生活中面臨食衣住行育樂相當多事務,常會有資訊遺忘情況。目前常見的生活紀錄方式是透過社交媒體平台發表包含圖片和文字的文章紀錄個人每天的生活。另一方面,穿戴裝置收集的位置資訊、生理數據、影像資料也紀錄使用者豐富的生活經歷。本團隊運用穿戴裝置和社交媒體平台擷取大量資訊,建立完整的個人知識庫,並且導入外部語意知識以及世界知識庫,形成輔助記憶,提供資訊召回服務,協助人們的回想自己過去的生活經歷。
With the passage of time, people often forget something over time and encounter the situations where they need to recall past experiences in their daily life. In recent years, people are used to logging their life on social media platforms. On the other hand, visual lifelogs recorded by wearable devices capture detail of an individual’s life experiences, offering complementary information for lifestyle analysis.
A multimodal joint learning approach trained on both text and images from social media posts shared on Twitter is proposed to extract life events in tweets. Then, the extracted information is transformed into knowledge base facts. To reduce the semantic gap between visual data and semantic descriptions of life events, we introduce semantic knowledge for daily activity recognition. The constructed personal knowledge bases are compatible with world knowledge bases and are expected to be useful to information recall applications.
Reference :
- IPM 2020:https://reurl.cc/AkLebj
- ICMR 2020:https://reurl.cc/j8Yjmm
- SIGIR 2019:https://reurl.cc/eE74Vb
▲ 基於多模態聯合學習的生活紀錄探勘系統架構圖
Multimodal Joint Learning-Based Lifelog Mining System Overview
▲ TexSim- 影像生活活動辨識系 統架構圖
TexSim-Visual Lifelog Activity Recognition System Overview
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 3 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 3 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎提升口說語言之理解能力
Towards Better Spoken Language Understanding
►國立臺灣大學 林守德教授/ Prof. Shou-De Lin, National Taiwan University
►國立臺灣大學 陳縕儂副教授/ Associate Prof. Yun-Nung Vivian Chen, National Taiwan University
現今大部分之自然語言處理之技術皆應用於文字領域,而許多智慧裝置是藉由語音的方式進行輸入的,故文字的品質皆取決於語音辨識系統之效能。然而,語音辨識並非完美,文字內容可能包含聲音相近,而語意相差甚遠的詞彙,導致後續的語意理解錯誤,影響最終應用之效能。台大資訊系團隊透過詞彙間聲音之相似性,讓AI模型學習考慮其他可能的詞彙背後所包含的語義,進而提升在口語輸入上的理解能力,落實語意理解技術於真實應用之發展。
The current natural language processing technology focuses on texts, but a lot of devices are speech-based, and the text quality highly depends on automatic speech recognizers. However,speech
recognition may output words with similar acoustics but totally different meanings, resulting in misunderstanding in diverse applications. The National Taiwan University research lab proposed the approach to learn the potential semantics by considering texts with similar acoustics, improving the performance of spoken language understanding for practical applications.
Reference :
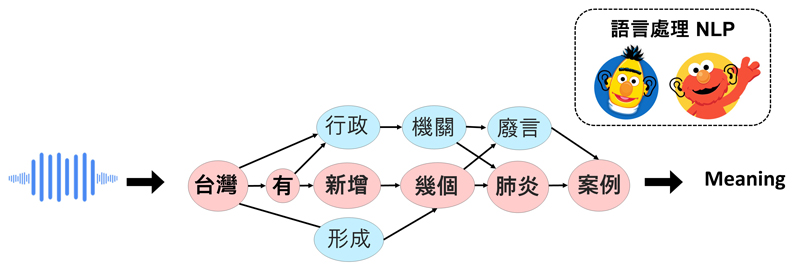
▲ 語音辨識導致理解困難示意圖
Illustration of speech misrecognition for understanding difficulty.
▲ 利用語音詞格提升語意理解能力
Improving understanding performance via speech lattice.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 21 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 21 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix