▎全自動乳房超音波乳癌偵測與診斷系統
ABUS Cancer Computer-aided Detection and Diagnosis System
►國立臺灣大學 張瑞峰教授 / Prof. Ruey-Feng Chang, National Taiwan University
運用人工智慧技術開發的全自動乳房超音波乳癌偵測與診斷系統,採用一次性檢查設計,1秒內即可完成一個全自動乳房超音波(300張影像)的乳癌檢閱程序,精確定位乳癌位置及顯示區域,同時進行診斷。本系統具有高檢測率、高診斷率、低偽陽性、並兼具強韌度(可偵測1公分以下的乳癌),在95%正確度下,每個影像檔的偽陽性率僅2顆,大幅加快閱片時間,此外,乳癌診斷準確度高達89.2%,在檢測上具有高度臨床價值。
The “ABUS Cancer Computer-aided Detection and Diagnosis System” is a breast cancer detection and diagnosis system designed with the artificial intelligence technology. is developed to locate the breast
tumor in automatic whole-breast ultrasound (ABUS) image. Through the one-take and the one-stage detection architecture, our compueter-assisted detection (CADe) system can completely review an ABUS image within 1 second. The system has properties of high detection rate, high diagnosis rate and accuracy, low false positive (FP) with robustness or tumor size < 1 cm. In detection, it has only 2 FPs in 95% sensitivity, and significantly reduces the detection time, which indicates the system is of great worth in clinical breast examination. Moreover, our system shows promising clinical applications with 89.2% accuracy in breast cancer diagnosis.
(a)
(b)
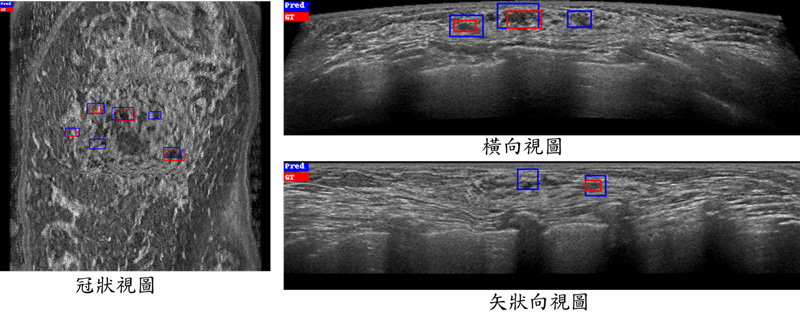
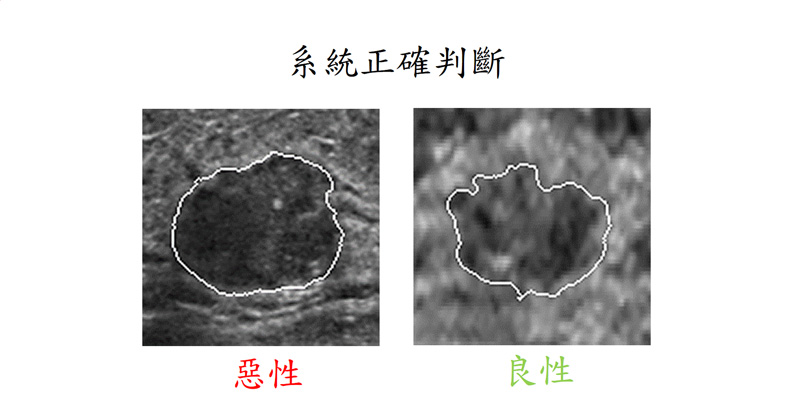
▲ 上圖是應用全自動乳房超音波乳癌偵測與診斷系統之結果,(a)是從冠狀視圖、橫向視圖、以及矢狀向視圖三種不同檢視方向上所顯示的偵測結果,紅色是真正的腫瘤區域,藍色則為系統所判斷的腫瘤範圍;(b)是診斷系統判斷兩個腫瘤的結果,此兩個腫瘤是臨床不易判斷正確的病例,但我們系統可以正確判斷其良惡性。
The Figure illustrates the results of our cancer detection and diagnosis system. The Figure (a) is the detection result displayed in three different viewing directions from the coronal view, transverse view, and sagittal view. The red is the ground truth tumor area, and the blue is the tumor area detected by our detection system. The Figure (b) is the two diagnostic result determined by our diagnosis system. These two tumors are clinically difficult to diagnose correctly, but our diagnosis system can classify correctly.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 26 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 26 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎持續發展睡眠呼吸中止症的全方位照護系統
Further Developments in Comprehensive Care System for Sleep Apnea
►臺北醫學大學 劉文德副教授 / Associate Prof. Wen-Te Liu, Taipei Medical University
為解決以往因缺乏長期追蹤導致呼吸中止症診斷和後續照護困難的問題,台北醫學大學與雙和醫院睡眠中心共同推出「Sleep_powergo」聊天機器人,以國內普及率高達95%的LINE作為互動平台,陸續建置睡眠相關問卷、呼吸中止症治療衛教資訊、環境及生理數據的即時量測和歷史量測報告生成模組,並運用AI發展個人化健康風險管理系統。目前於雙和醫院內示範推行,後續可推廣至居家和長照情境,提供使用者全方位的照護。
In order to solve the problem of difficulty in diagnosis of sleep apnea and follow-up care due to the lack of long-term tracking, Taipei Medical University and Shuang-Ho
Hospital Sleep Center jointly launched the chatbot called “Sleep_powergo” on LINE (with domestic penetration rate of 95%) as an interactive platform, it has successively built sleep-related questionnaires, apnea treatment and health education information, real-time measurement of environmental and physiological data, and historical measurement report generation modules, and used AI to develop a personalized health risk management system. It is currently being demonstrated in Shuang-Ho Hospital, and can be extended to home and long-term care settings in the future to provide users with a full range of care.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 24 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 24 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎結合多元裝置建構 AI 生理分析及預警系統
Combining Multiple Devices to Build AI-enabled Physiological Analysis and Early Warning Systems
►臺北醫學大學 劉文德副教授 / Associate Prof. Wen-Te Liu, Taipei Medical University
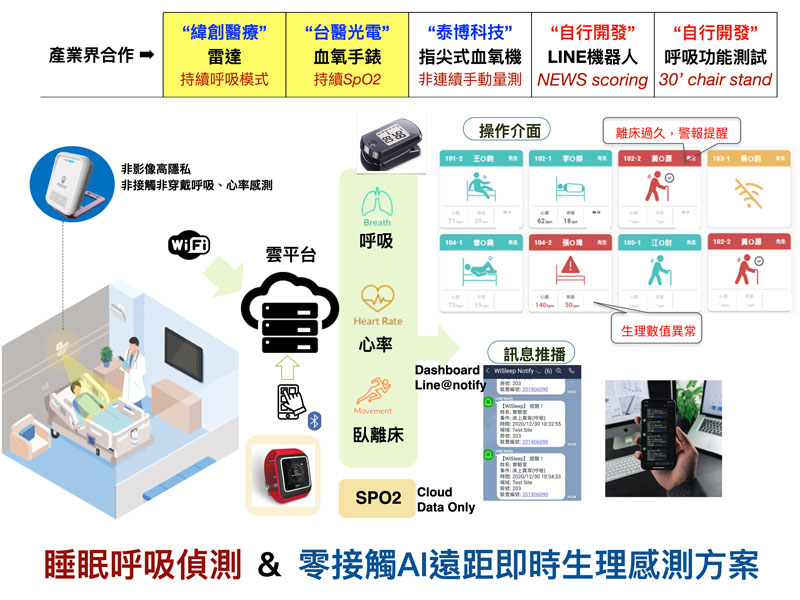
因應新冠肺炎(COVID-19)疫情,衛生福利部雙和醫院整合個人式肺功能儀、手指型血氧濃度計、智慧腕表、貼片式心率微型感測器和毫米波感測器等多項可攜式及穿戴式裝置,將使用者的所有生理參數整合,並配合手機應用程式提醒填答問卷及各項主觀量表結果,建構人工智慧生理分析及預警系統,協助臨床照護人員。所有使用之裝置無侵入性、放射線暴露疑慮,且不需醫護人員近距離接觸,不但提升防疫量能,更落實醫療與科技結合之在地化發展。
In response to COVID-19 epidemic, the Shuang-Ho Hospital of the Ministry of Health and Welfare integrated a number of portable and wearable devices such as personal pulmonary function meters, finger- type oximeters, smart watches, patch-type
heart rate micro sensors, and millimeter wave sensors. All the physiological parameters of the users, and the outcomes of questionnaire and various subjective scales reminding to fill through mobile phone application were used to construct an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled physiological analysis and early warning system to support clinical decisions for healthcare personnel. The above devices employed are free from invasiveness and radiation exposure, and do not require close contact with medical staff. Such AI-enabled systems are believed to not only improve the capacity of epidemic prevention, but also promote the local development of combining clinical healthcare with information technology
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 24 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 24 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎多疾病胸部 X 光電腦輔助診斷系統
Multi-disease Thorax X-ray CADx System
►國立臺灣大學 張瑞峰教授/ Prof. Ruey-Feng Chang, National Taiwan University
本團隊採用深度學習技術開發的多疾病胸部X光電腦輔助診斷系統有四大特點: 1. 能診斷出14種常見的胸腔疾病,包括肺不張、實變、浸潤、氣胸、水腫、氣腫、纖維化、積液、肺炎、胸膜增厚、心臟肥大、結節、腫塊和疝氣。2. 高效圖像表徵提取。3. 增強疾病關聯性資訊,幫助X光影像分類不同胸腔疾病。4. 比最先進的 (SOTA) 技術擁有更好的效能(平均AUC 可達 0.8266),減少了閱片者間變異,客觀地提供診斷結果。
Chest X-ray is one of the most common imaging examinations in the clinical diagnosis of lungs. Our thorax X-ray CADx system is useful for diagnosing different thorax diseases, which has excellent diagnostic accuracy and reduces viewer variances.
Our system has the following four advantages:
1. Diagnosis of 14 thorax diseases: Atelectasis, Consolidation, Infiltration, Pneumothorax, Edema, Emphysema, Fibrosis, Effusion, Pneumonia, Pleural thickening, Cardiomegaly, Nodule, Mass, and Hernia
2. Efficient image representation feature extractor
Extract representative image information.
3. Enhance the correlation between different
thorax diseases
Fibrosis → Atelectasis, Pleural Effusion → Atelectasis.
4. Accurate diagnostic performance
Better diagnostic performance than state of the art (mean AUC = 0.8266).
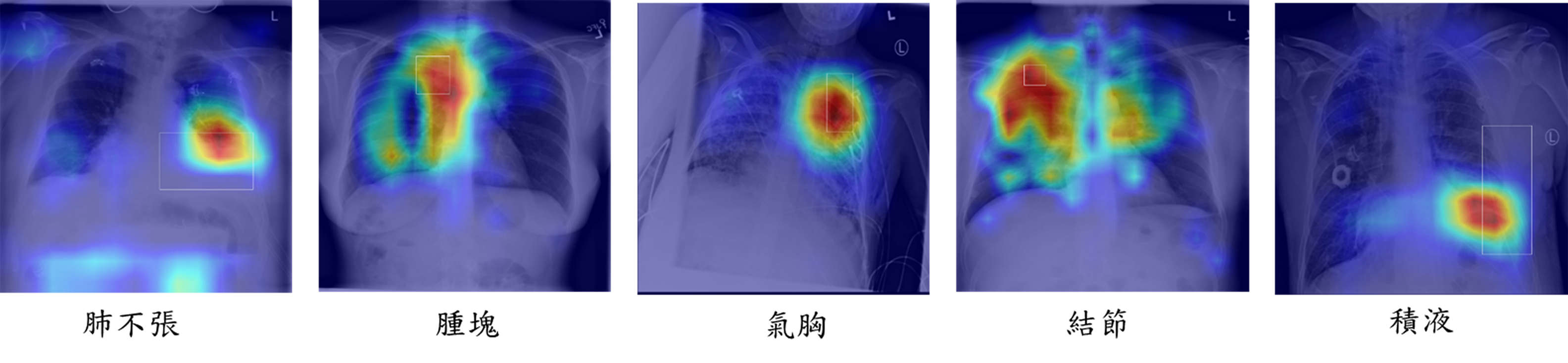
▲ 上圖是通過 Grad-CAM 方法對不同胸部疾病的可視化結果(包括肺不張、腫塊、氣胸、結節和積液)。白色方塊是 NIH CXR 數據集提供的邊界框,由放射科醫生標定疾病位置,熱力圖顯示我們的方法可以準確定位病變區域。
The Figure Visualization results through the Grad-CAM method for different thorax diseases, including atelectasis, mass, pneumothorax, nodule, and effusion. The white squares are the bounding boxes provided by the NIH CXR dataset, which localized the disease according to a radiologist, and the heat map shows our method can accurately locate the lesion area.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 26 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 26 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
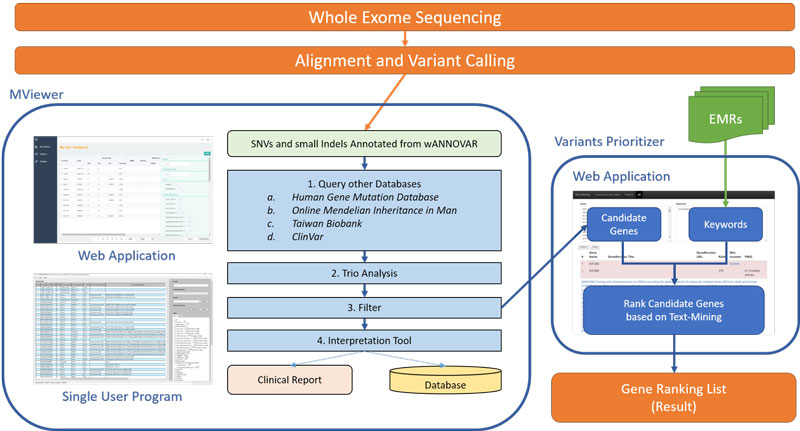
▎智慧型基因變異篩選系統
AI_Variant Prioritizer
►國立臺灣大學 賴飛羆教授/ Prof. Fei-Pei Lai, National Taiwan University
次世代基因定序結果的判讀是一大挑戰。為了更快速地找尋真正具有致病性且與臨床上症狀相關之變異點,我們開發AI_Variant prioritizer人工智慧模組,藉此來找出最有可能導致疾病的變異點位,提升疾病的診斷率,以及減少人工判讀的負擔。此模組主要協助變異的快速辨識與排序,結合文字探勘與人工智慧功能,提升判讀時對可能變異的警覺性,以期達到變異判讀的最佳效率。未來,也可也擴及相關分子診斷,例如藥物基因體檢測等,將可加速醫療相關產業的發展。
The interpretation of next generation sequencing (NGS) is a big challenge. In
order to improve the molecular diagnosis, we developed the AI_Variant prioritizer, a machine learning-based variant prioterization system to prioritize candidate variants for human disease, increase the disease diagnostic yield, and decrease the load of manpower. It assists variant interpretation for NGS, by rapid identification and prioritization of variants. It can also apply to other molecular diagnostics, such as pharmacogenomic testing, to facilitate the healthcare system.
Reference :
▲ AI_Variant Prioritizer
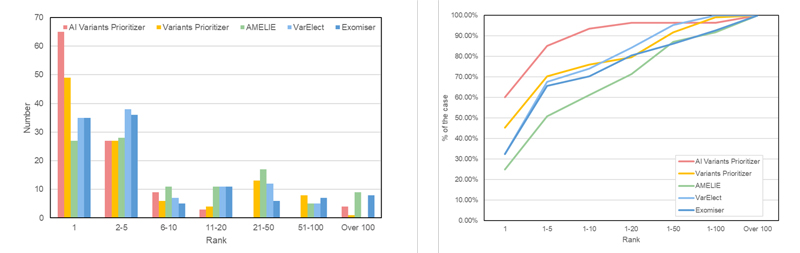
▲ 智慧型基因變異篩選系統預測結果比較。與目前可以免費使用之軟體相較,本系統的預測準確度最高
Performance of the AI_Variant Prioritizer. Compare with worldwide software, our system has highest prediction accuracy.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 28 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 28 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix