▎舉一反三之電子病歷資訊萃取模型
The Electronic Health Record Information Extraction Model
►臺大醫院 黃建華臨床教授/ Clinical Prof. Chien-Hua Huang, National Taiwan University Hospital
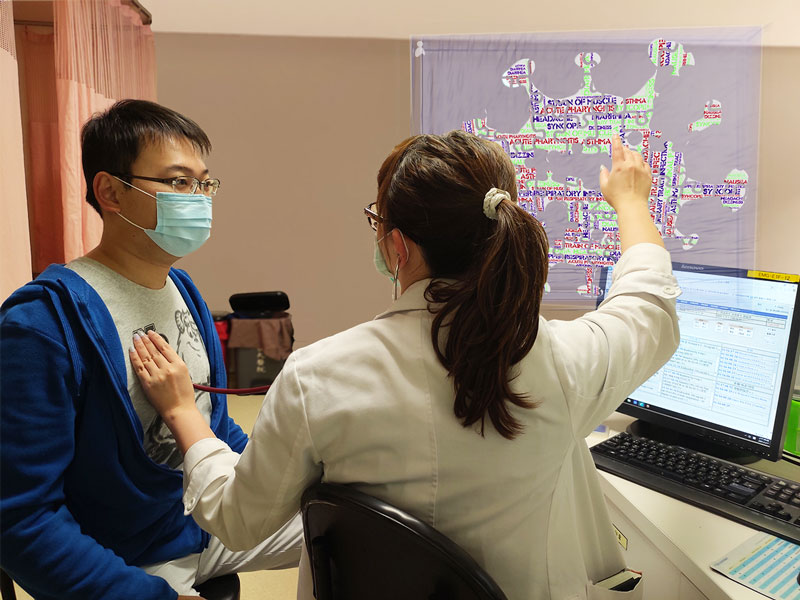
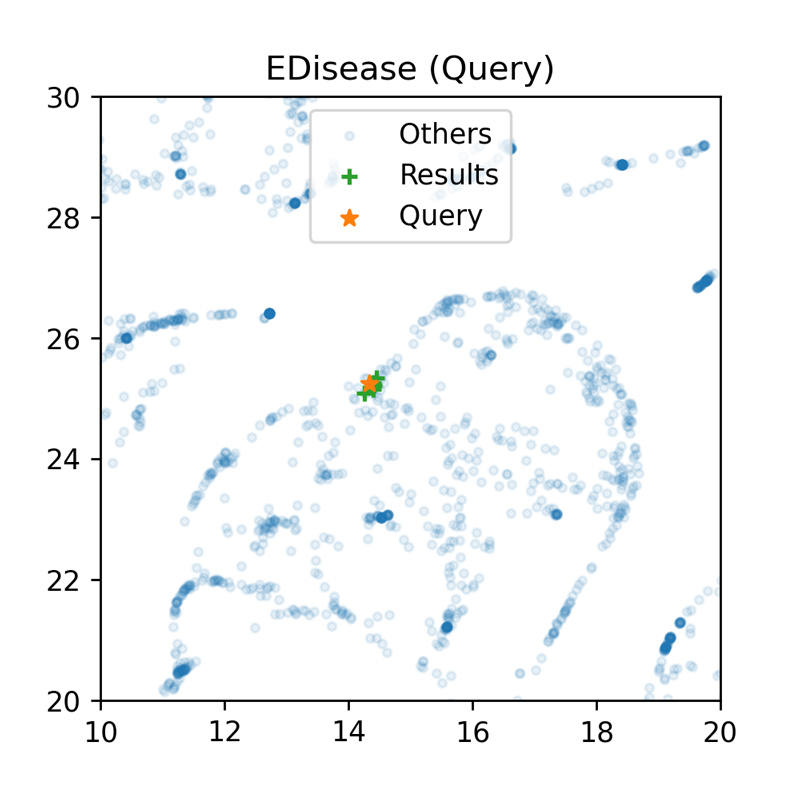
電子化病歷資料庫(EHRs)內含了豐富的醫療經驗,為充分利用此醫療智慧寶庫,臺大醫院急診部在醫療人工智能研究與應用中,建立EDisease模型以非監督式學習模式萃取EHRs的內涵經驗特徵,並以此發展各項後續的應用,以期望實現科技輔助強化醫療能力的新世代智慧醫療。
In order to leverage AI to improve physician’s ability, the team from National Taiwan University Hospital Emergency Department
built an information extraction model – EDisease, through which the medical knowledge and experience in electronic health records could be concluded to meaningful feature vectors for further application.
Reference :
◀新世代的智慧醫療中,將能充分利用人工智慧強化醫師的醫療能力。( 圖片來源: Chen et al.)
Physician’s ability could be enhanced by AI technology in the next generation healthcare. (Source: Chen et al.)
◀ 舉一反三,讓人工智慧告訴你相似的病歷。( 圖片 來源:Chen et al.)
AI could give you the most relevant clinical cases. (Source: Chen et al.)
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 31 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 31 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix
▎以人工智慧改善急診患者就診流程及來診暫留之預後
Improve Emergency Department Patient Journey Using Explainable AI
►臺大醫院 黃建華臨床教授/ Clinical Prof. Chien-Hua Huang, National Taiwan University Hospital
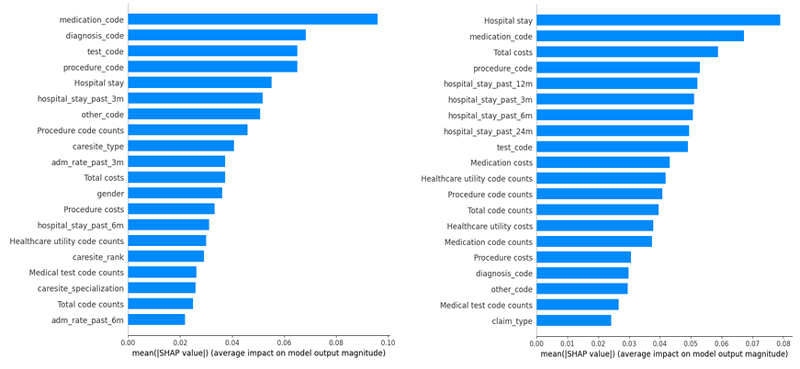
臺大醫院急診部與加拿大新創公司Knowtions Research合作,透過Text2Node、HVec等專利技術訓練全民健保數據集,建立深度學習模型預測心臟停止病患在救治後未來的死亡率與再入院率,並建立可解釋性模型來提供風險因子,協助急診醫師診斷。模型AUROC最高可達0.884。以上研究已於多個國際研討會發表。同時也與健保署合作,未來預計結合健康存摺,以期在急診建立人工智慧輔助的分流與早期預警系統。
National Taiwan University Hospital Emergency Department (NTUH-ED), collaborating with Knowtions Research, built deep learning models to predict mortality and readmission of in-hospital cardiac arrest patients with national health insurance claims data.
The models are among the top performing ones in the world, with an AUROC 0.884. The models also use explainable deep learning technologies to provide risk factors to support the doctor’s decisions. Future steps will be establishing an early warning system in the NTUH-ED by including My Health Bank data, to help doctors to optimize resources, improve patient outcomes and reduce overcrowding.
Reference :
◀ 於與日本京都大學合辦之 2020 The 5th NTU-KU Joint Symposium on Digital Health 發表演講。
Delivered a speech at “2020 The 5th NTU-KU Joint Symposium on Digital Health” co-organized with Kyoto University, Japan
◀ 預測 30 天死亡率和 30 天再入院率的總體特徵權重。
Overall feature weight on the full test dataset for predicting 30-day mortality and 30-day readmission.
此研究歸屬科技部 AI 專案計畫執行成果,詳細資訊請參考附錄之計畫總表第 31 項
For the name of the project which output this research, please refer to project serial no. 31 on the List of MOST AI projects on Appendix